Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
Polish forests
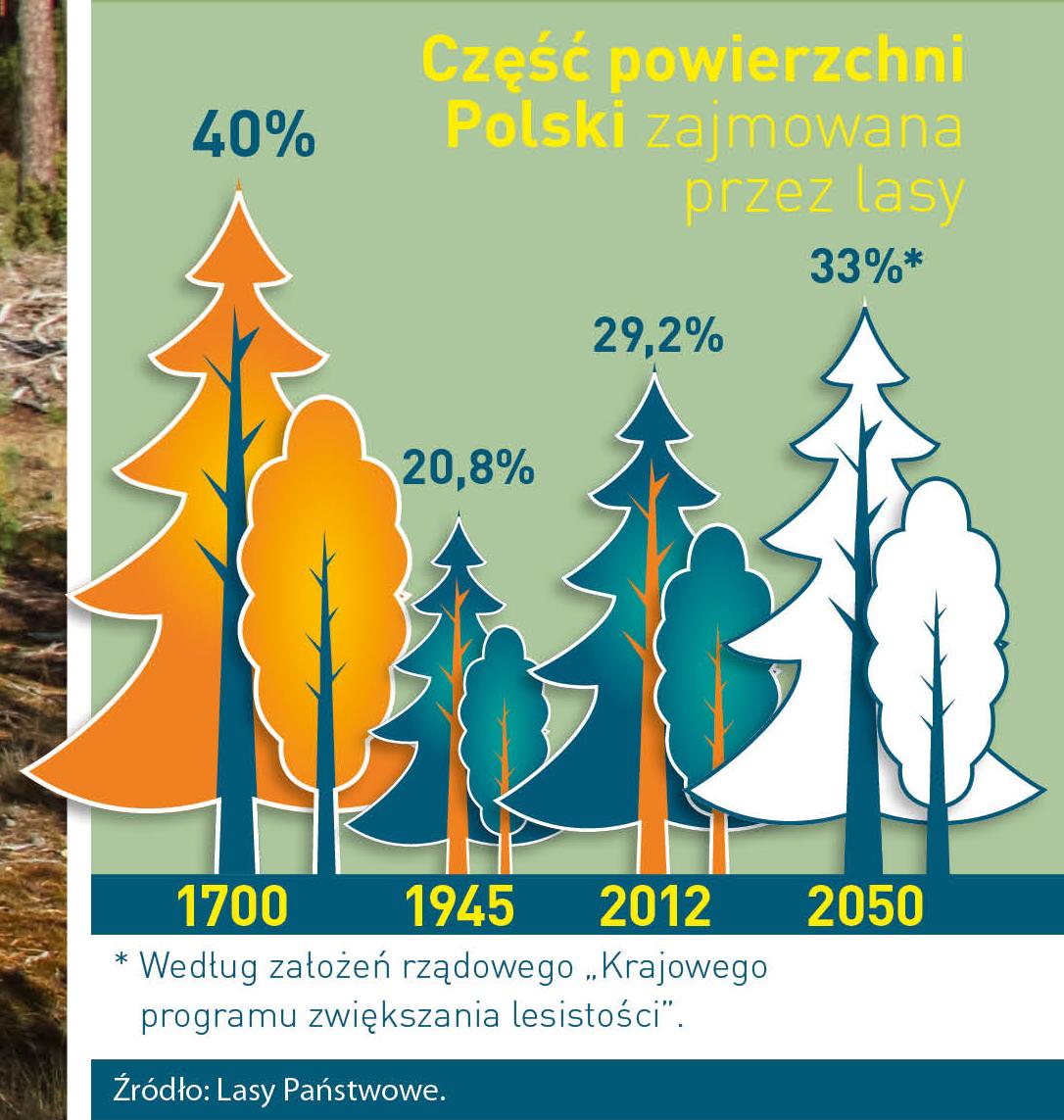
Poland is in the European lead, while concerning the area of all forests. They cover about 29,2 % of the country territory, and grow within the area of 9,1 million hectares. The overwhelming majority of the forests is state owned, of which almost 7,6 million hectares are managed by the State Forests National Forest Holding..
The number of Polish forest is still growing. The forestation rate of the country has increased from 21 % in 1945 to 29,2 % at the moment. Between 1995 and 2008, the forest area increased by 310 thousand ha. The basis for afforestation works is the "National Programme for Increasing the Forest Cover" (KPZL), assuming an increase of the forestation rate up to 30 % by 2020 and up to 33 % by 2050. Polish forests abound in flora, fauna and fungi. 65 % of the total number of animal species live there.
The forests grow in our country on poor soils, mainly because of the development of the agriculture in previous years. It influences the distribution of the types of the forest sites in Poland. Over 55 % of the forest areas is covered with coniferous forests. In other areas, there are forest sites, mainly the mixed ones. Their small part constitute alder and riparian forests – not more than 3 %.
In the years 1945 – 2011 the area of natural deciduous tree stands within the area of the State Forests National Forest Holding increased from 13 to 28,2 %.
Within the lowlands and uplands the most often occurring tee species is pine. It covers 64,3 % of the forest area of the State Forests National Forest Holding and 57,7 % of private and commune forests. In the mountains the predominant species is European spruce ( in the west) and European spruce with beech (in the east). Domination of pine is the result of carrying on sustainable forest management in the past. Once, the monocultures (crops or cultivations of one species) were the answer to the great demand of industry for wood. Such forests appeared to be quite fragile to climatic factors. They also were often the prey of pests' expansion.
In Polish forests, the share of other tree species, especially deciduous trees have been systematically increasing. The foresters have stepped aside from monocultures – that is why, they try to fit specific species of the forest stand to the natural stand, that would be proper for the given area. Thanks to that, in the years 1945 – 2011, the area of the deciduous tree stands within the lands of the State Forests National Forest Holding increased from 13 to 28,2 %. There occur more and more frequently the following tree species: oaks, ashes, maples, sycamore maples, elms, but also birches, beeches, alders, poplars, hornbeams, aspens, tilias and willows.
Our forests are the most often represented by the forest stands aged 40 to 80 years. The average age of the forest equals 60 years. More and more trees are of big size at the age over 80 years. Since the end of the Second World War, the forests' area has increased up to almost 1,85 million hectares.
Raport o stanie lasów w Polsce 2012
 Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
Współpraca polskich i słowackich leśników
Współpraca polskich i słowackich leśników
Dyrektorzy Państwowego Gospodarstwa Leśnego Lasów Państwowych oraz Generalnej Dyrekcji Lasów Słowackich podpisali 20 lipca 2022 r. w Bielsku-Białej porozumienie o nawiązaniu współpracy w ramach Programu Współpracy Transgranicznej INTERREG Polska – Słowacja 2021 – 2027. To pierwszy krok do wspólnego pozyskania środków m.in. na renowacje ważnych obiektów architektury drewnianej leżących po obu stronach granicy.
Stronę polską reprezentowali: Józef Kubica Dyrektor Generalny Lasów Państwowych oraz Dyrektor Regionalnej Dyrekcji Lasów Państwowych w Katowicach - Damian Sieber. Po stronie słowackiej dokumenty parafował Jan Marhefka, dyrektor Generalnej Dyrekcji Lasów Republiki Słowacji.
Goście zwiedzili leśniczówkę w Lipniku, która jest jednym z pierwszych obiektów, który ma zostać odrestaurowany.
- Bardzo się cieszę, że projekty takie jak INTERREG pozwalają chronić nasze dziedzictwo, restaurować obiekty historyczne i przeznaczać je do dalszego użytkowania dla społeczeństwa. To wielka sprawa dla nas, dla Lasów Państwowych, aby ten obiekt jakim jest leśniczówka w Lipniku powstała według projektu austriackiego architekta Emanuela Rosta w 1884 r. została odrestaurowana i w niedługim czasie ponownie biła blaskiem 0jak w dniu jej oddania do użytku – powiedział dyrektor Józef Kubica..
Remont leśniczówki w Lipniku jest jednak tylko jednym z elementów planowanego przedsięwzięcia. Ideą nadrzędną planowanego projektu jest połączenie obiektu lipnickiej leśniczówki i podobnego obiektu na terenie lasów słowackich, wspólnym szlakiem architektury drewnianej, zarówno tej historycznej jak i tej współczesnej, sakralnej oraz świeckiej.
- To przedsięwzięcie jest idealnym przykładem do promowania drewna, jako w pełni odnawialnego, a jednocześnie mającego wiele zalet praktycznych, surowca budowlanego, spełniającego warunki zrównoważonego rozwoju i życia w zgodzie z naturą. Drewna, które zarówno dla Słowaków jak i Polaków jest wielkim bogactwem, ale również wielkim zobowiązaniem, do prowadzenia zrównoważonej, zgodnej z naturą gospodarki leśnej, którą przy tej okazji również chcemy wspólnie promować - dodaje Jan Marhefka, dyrektor słowackich Lasów.
Niezależnie od działania związanego z podpisaniem polsko-słowackiej umowy, na zlecenie Nadleśnictwa Bielsko został wykonany projekt konserwatorski renowacji „Starej leśniczówki”, poprzedzony wnikliwymi studiami i inwentaryzacją konserwatorską jej stanu. W najbliższych tygodniach zostanie ogłoszone postępowanie przetargowe na wykonanie dokumentacji budowlanej a także jak twierdzi nadleśnictwo dołoży wszelkich starań, aby w momencie ogłoszenia naboru wniosków do programu INTERREG, dokumentacja wykonawcza dla renowacji była gotowa do przedstawienia komisji konkursowej.


 fot. Paweł Fabijański
fot. Paweł Fabijański
 fot. Paweł Fabijański
fot. Paweł Fabijański
 fot. Paweł Fabijański
fot. Paweł Fabijański